Tuberculosis is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide.
What is Tuberculosis?
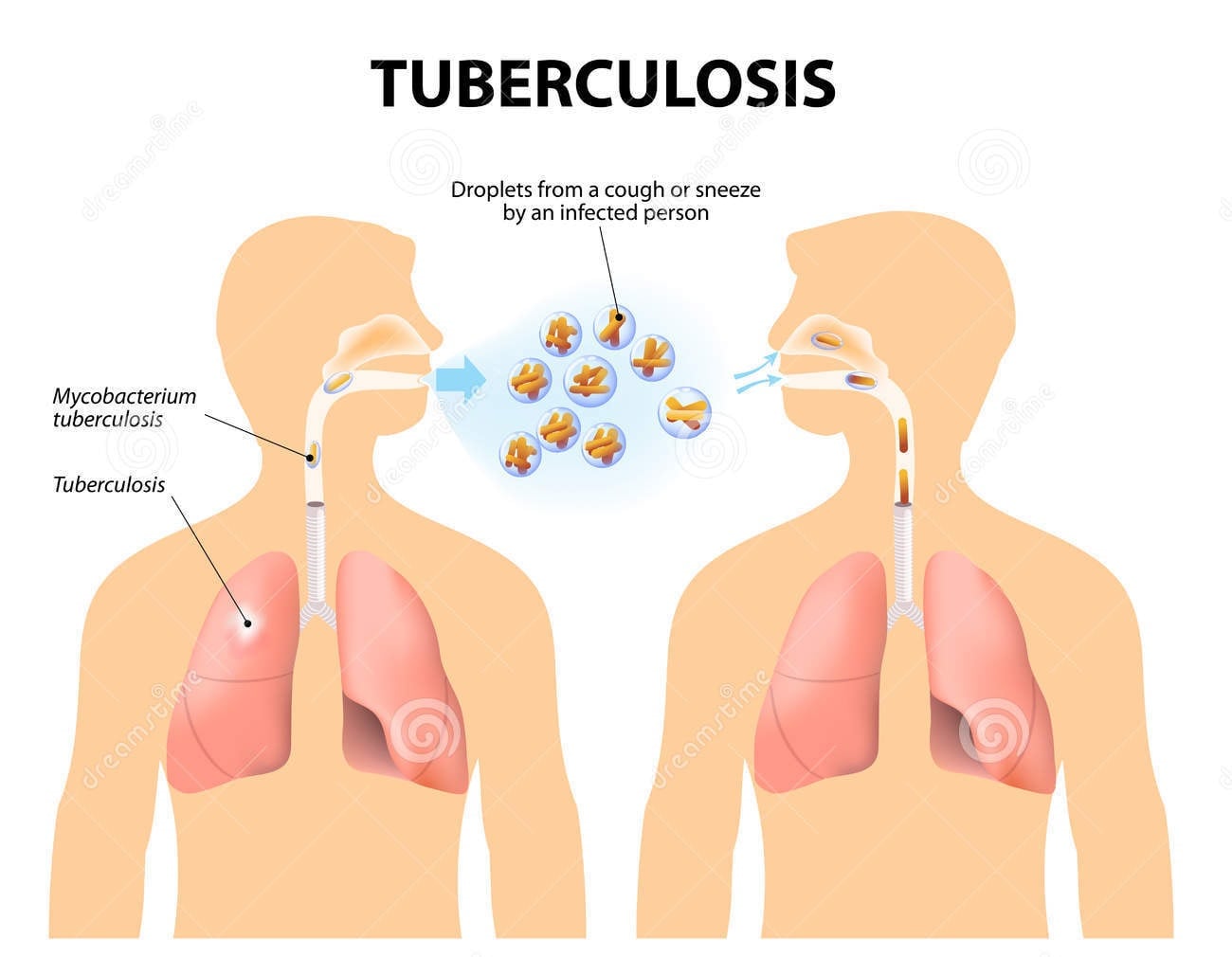
Tuberculosis or commonly referred to as TB is a potentially infectious and contagious disease that mainly attacks the lungs but can also spread to other parts like brain and spinal cord. It is caused by a single bacteria called mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). This disease is the second biggest killer globally.
Types - there are two forms of TB
- Latent TB – In this state, the bacteria is present in the body but, it is in an inactive state. They do not cause any symptoms and it is not contagious. But it can become active anytime
- Active TB – the bacteria in the body is active and multiplies. It is contagious and shows symptoms.
Causes and Transmission
Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria that spreads from person to person through microscopic droplets released into the air. This can happen when someone with the untreated, active form of tuberculosis coughs, speaks, sneezes, spits, laughs or sings. Although tuberculosis is contagious, it's not easy to catch.
Risk Factors
Tuberculosis mostly affects adults in their most productive years. However, all age groups are at risk. Over 95% of cases and deaths are in developing countries. A number of other factors are present. The important risk factor is HIV. The risk of active TB is also greater in persons suffering from other conditions that impair the immune system.Use of tobacco is also considered a risk. Working in a hospital or nursing home can also increase the risk.
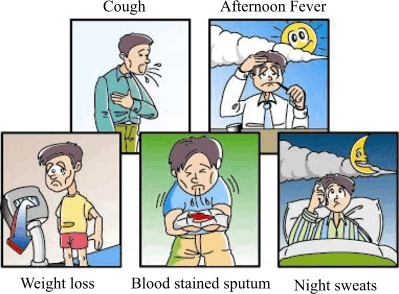
Signs and Symptoms
- Coughing that lasts longer than 3 weeks
- Sputum is seen sometimes with blood
- Chest pains
- Fever
- Weakness
- Weight loss
- Night sweating
- Chills
- Loss of appetite
Diagnosis
It is difficult to analyze it based on physical examination. The common tests which can determine its presence are –
- Skin test - small injection of PPD tuberculin, an extract of the TB bacterium, is made just below the inside of forearm. The injection site should be checked after 2-3 days and if a hard, red bump has swollen up to a specific size, then it is likely that TB is present Blood tests
- Chest X-Ray
- Sputum tests – the sputum samples are observed under microscope to check for TB Bacteria
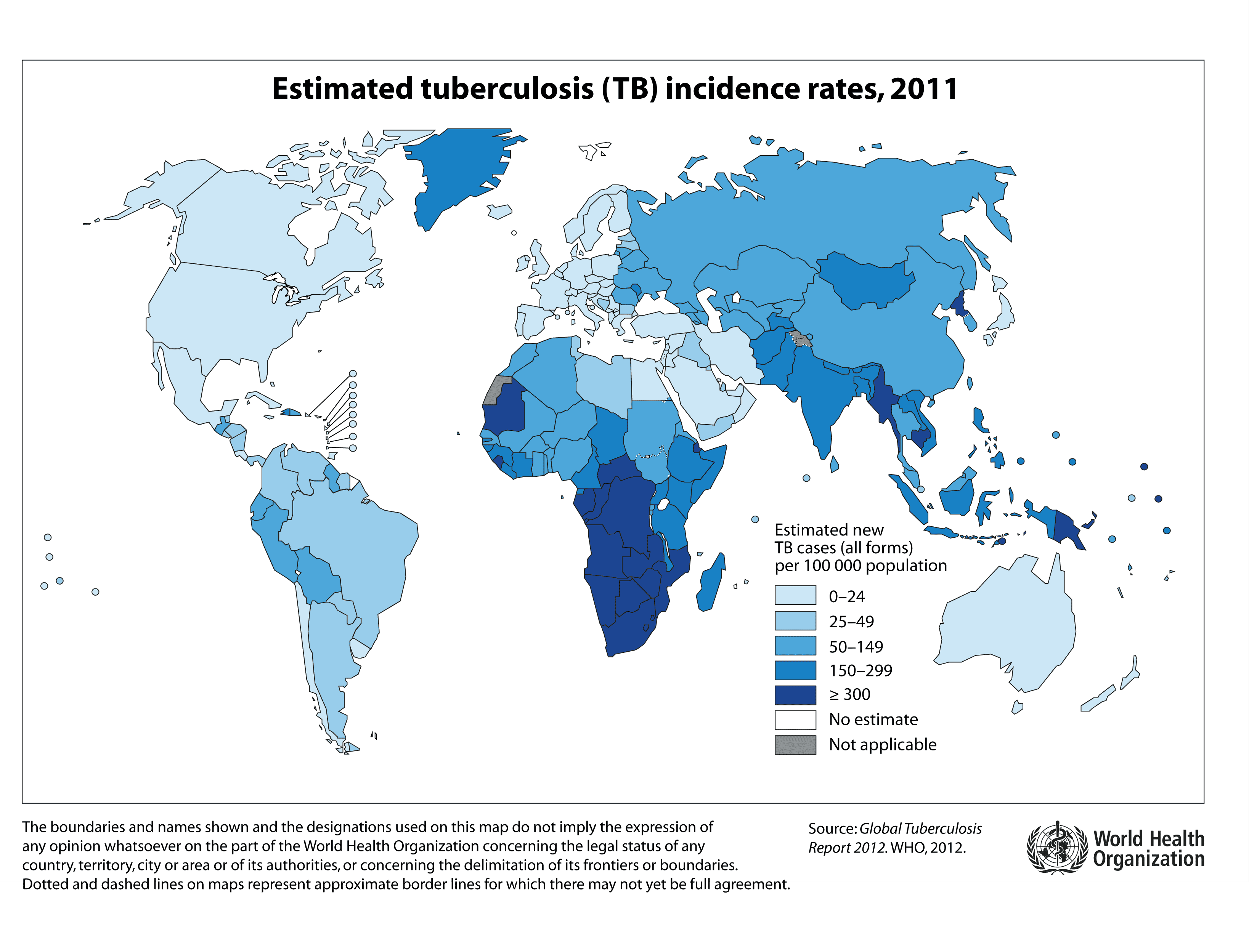
Statistics
In 2015, 10.4 million people fell ill with TB and 1.8 million died from the disease (including 0.4 million among these with HIV). Over 95% of TB deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries.
.jpg)